Science
U.S. Citizens Embrace AI for Mental Health Crisis Detection
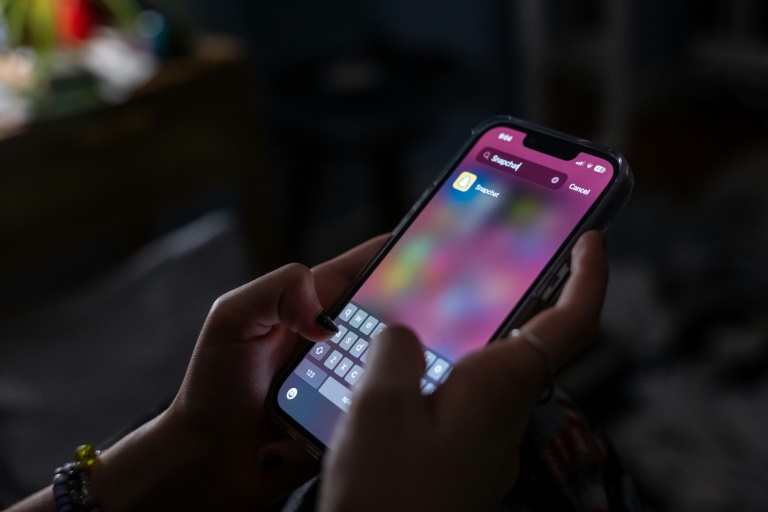

The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into mental health crisis detection is gaining traction among U.S. citizens, as revealed by a recent survey conducted by Iris Telehealth. The findings indicate a significant openness to AI tools for monitoring mental health, particularly in urgent situations. This development comes at a time when the demand for mental health services is rising, yet access to qualified clinicians remains inadequate.
According to the survey, which analyzed responses from 1,000 Americans, nearly half of the participants, specifically 49%, expressed willingness to utilize AI technologies that monitor indicators such as vocal tone and facial expressions during digital interactions. However, a strong preference emerged for retaining human oversight, with 73% of respondents insisting that a human clinician should lead any decisions arising from AI alerts. Only 8% of those surveyed felt comfortable with AI acting independently in crisis situations.
Demographic Insights on AI Acceptance
The survey also shed light on demographic variations in acceptance levels towards AI in mental health crisis detection. Men showed a greater comfort level compared to women, with 56% of men willing to engage with AI monitoring, contrasted with only 41% of women. Furthermore, younger generations, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, demonstrated a higher openness to AI involvement, with 29% and 24% respectively, while only 5% of Baby Boomers reported being “very comfortable” with the concept.
Income brackets also seemed to influence receptiveness. Lower-income individuals, those earning $25,000 or less, showed a higher willingness to adopt AI monitoring tools, with 61% expressing support compared to 44% among higher-income earners. This suggests that AI could play a crucial role in bridging access gaps for underserved populations.
Concerns Surrounding AI in Mental Health Care
Despite the growing acceptance, significant concerns about AI in mental health crisis detection remain. The survey highlighted three primary apprehensions. Firstly, 60% of respondents feared that reliance on AI could diminish the human connection vital for empathetic care. Many individuals want to feel understood rather than merely categorized by data points.
Secondly, 55% of participants expressed worries about the potential for AI to misinterpret behaviors, resulting in false positives or missing genuine crises. In high-stakes scenarios, even minor errors can have grave consequences. Lastly, 36% of those surveyed voiced concerns regarding algorithmic bias, fearing that AI systems could reflect biases inherent in their training data, potentially leading to misidentifications across various demographics.
These insights emphasize the importance of incorporating human oversight into AI applications. Flanagan stressed that AI should serve as an enhancement to human judgment rather than a replacement, ensuring that patient care remains at the forefront.
The survey further revealed that when an AI flags a potential crisis, individuals prefer human involvement in follow-up actions. Responses indicated varied preferences: 28% of respondents wanted a family member or friend notified first, while 27% preferred a trained counselor to reach out within thirty minutes. Notably, 32%22% trusted AI to connect them directly with a human professional without prior consent.
Building Trust in AI-Powered Tools
To foster trust in AI-driven mental health crisis detection tools, several factors emerged as vital. Transparency was cited by 56% of respondents as crucial, with a demand for clear explanations of how AI identifies risks. Ensuring that a licensed clinician reviews AI recommendations before any intervention would build confidence, according to 32% of participants. Additionally, user control over monitoring and the ability to override AI alerts were important considerations for 25% and 16% of respondents, respectively.
Healthcare organizations considering the integration of AI must prioritize maintaining human involvement in critical decisions. Preferences for follow-up actions vary, emphasizing the need for tailored approaches that accommodate diverse demographic groups. Younger populations may be more inclined to accept automated solutions, while older and higher-income patients may prefer traditional methods.
Embedding AI into familiar platforms, such as telehealth portals or electronic health records, can facilitate smoother adoption. Ensuring transparency, explainability, privacy protections, and robust human oversight will be essential in building trust and effectively leveraging AI’s potential.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, the thoughtful integration of AI could help alleviate pressures on overwhelmed emergency departments, enhance early detection of mental health crises, and ultimately improve patient outcomes while preserving the crucial human connection that patients value.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoToyoake City Proposes Daily Two-Hour Smartphone Use Limit
-
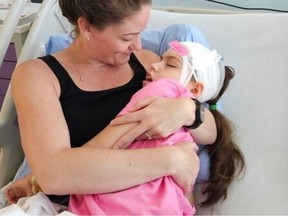
 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoB.C. Review Reveals Urgent Need for Rare-Disease Drug Reforms
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoPedestrian Fatally Injured in Esquimalt Collision on August 14
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDark Adventure Game “Bye Sweet Carole” Set for October Release
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoJimmy Lai’s Defense Challenges Charges Under National Security Law
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoKonami Revives Iconic Metal Gear Solid Delta Ahead of Release
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoSnapmaker U1 Color 3D Printer Redefines Speed and Sustainability
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoAION Folding Knife: Redefining EDC Design with Premium Materials
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoSolve Today’s Wordle Challenge: Hints and Answer for August 19
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGordon Murray Automotive Unveils S1 LM and Le Mans GTR at Monterey
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoVictoria’s Pop-Up Shop Shines Light on B.C.’s Wolf Cull
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoApple Expands Self-Service Repair Program to Canada