Business
Income Inequality in Canada Reaches Record High, Statistics Canada Reports
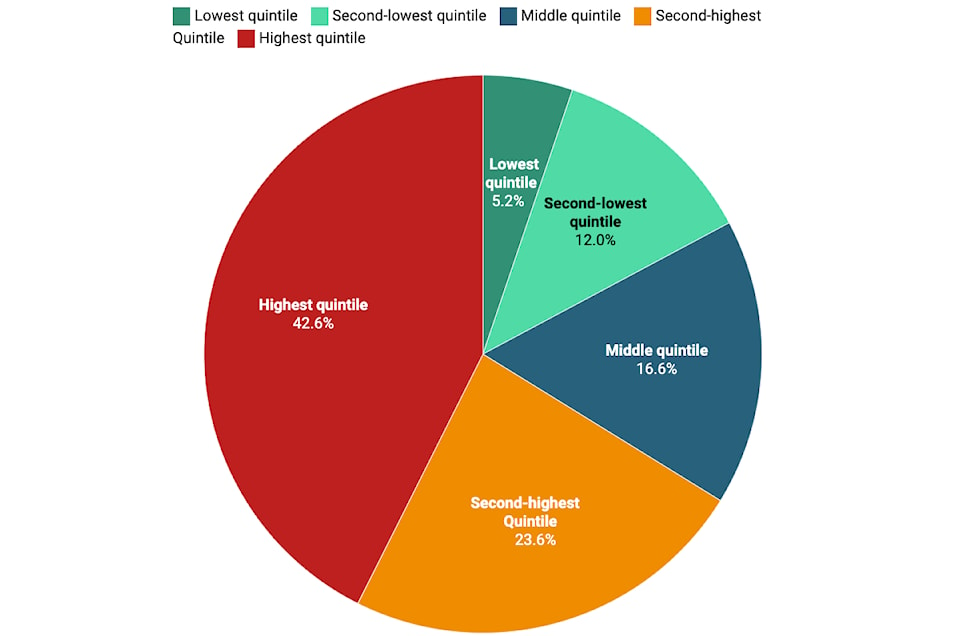
The income gap between wealthy and low-income Canadians has reached an unprecedented level, according to a recent report from Statistics Canada. In the first quarter of 2025, the top 40 per cent of households captured 66.2 per cent of all after-tax income, while the bottom 40 per cent received only 17.2 per cent. This represents an increase of 11.9 per cent from four years earlier, highlighting a growing divide in wealth distribution.
The widening income gap is attributed to significant gains for high-income households, particularly the top 20 per cent. Rising investment income has played a crucial role, while wages for the lowest earners have stagnated. According to experts, this trend reflects decades of policy choices and escalating executive compensation. The most pronounced growth has been seen among the top one per cent of earners, whose income has surged by 396 per cent since 1982, compared to a modest increase for the bottom 50 per cent.
Drivers of Income Inequality
Economist Marc Lee of the Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives criticizes the quintile method of measuring income inequality, stating it oversimplifies the differences within the top 20 per cent. He points out that while he falls into this category, his financial situation is vastly different from that of prominent billionaires. The average employment income for households in the top quintile was $208,313 in 2023, illustrating a stark contrast within income brackets.
Research indicates that income inequality has far-reaching consequences, including sluggish economic growth and deteriorating health outcomes. The International Monetary Fund has warned that widening income disparities can erode social cohesion and fuel political polarization. Furthermore, studies published in the American Journal of Public Health link income inequality to adverse health effects.
Several factors contribute to this growing inequality. Declining unionization rates and the concentration of market power in a few industries have diminished workers’ negotiating power regarding wages. Statistics Canada highlights two primary reasons for the widening income gap: significant gains in property income for high-income households and faster growth in earnings for top earners compared to others.
Wage Disparities and Executive Compensation
The disparity in wage growth is particularly evident in executive compensation. A report from the Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives reveals that the top 100 highest-paid CEOs earned an average of $13.2 million in 2023, with bonuses constituting the majority of this amount. The CEO-to-worker pay ratio has dramatically increased, with top executives now earning 210 times the average worker’s pay, up from a ratio of 104 in 1998.
“We never used to tolerate such high levels of compensation and inequality,”
Lee remarked, emphasizing the shifting tolerance towards wealth concentration among executives. This trend has forced companies to enhance their pay packages to attract top talent, further exacerbating income inequality.
The issue is compounded by the rising property income, which Statistics Canada defines as earnings from investments and real estate. Approximately two-thirds of all property income was earned by the top 20 per cent of households last year, up from 56 per cent in 1999. In contrast, the bottom 40 per cent received a mere 8 per cent of this income, demonstrating a growing divide in asset ownership.
Tax policies have also played a significant role in exacerbating income inequality. Silas Xuereb, a policy analyst with Canadians for Tax Fairness, notes that the Canadian tax system has evolved to benefit the wealthy. Historical data reveals that in 1949, the top marginal income tax rate was 84 per cent for high earners. Reforms in subsequent decades have progressively lowered this rate, resulting in reduced tax burdens on high-income earners, particularly from capital gains.
The increasing concentration of wealth among the top one per cent has raised concerns about social equity. Xuereb argues that addressing this income gap presents an opportunity for the government to increase revenues through measures such as higher taxes on the ultra-wealthy or implementing a wealth tax. While the federal government has previously indicated intentions to tackle income inequality, recent decisions have stalled progress.
Call for Action
Experts like Peter Dietsch from the University of Victoria stress the need for political leaders to acknowledge the shortcomings of current economic policies. He argues that a fundamental shift in understanding the relationship between government policy and income inequality is necessary for meaningful change.
“Once that actually catches on, then we might be closer to solving that or to addressing that problem,” Dietsch stated. The challenge remains significant, as raising taxes on the wealthy is often met with resistance.
The alarming statistics presented by Statistics Canada underline a critical issue that affects not just economic stability but also the social fabric of Canada. As the wealth gap continues to widen, it becomes increasingly important for policymakers and citizens alike to engage in dialogues about equitable distribution of resources and the long-term implications of growing income inequality.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoToyoake City Proposes Daily Two-Hour Smartphone Use Limit
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoPedestrian Fatally Injured in Esquimalt Collision on August 14
-
 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoB.C. Review Reveals Urgent Need for Rare-Disease Drug Reforms
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDark Adventure Game “Bye Sweet Carole” Set for October Release
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoJimmy Lai’s Defense Challenges Charges Under National Security Law
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoVictoria’s Pop-Up Shop Shines Light on B.C.’s Wolf Cull
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoKonami Revives Iconic Metal Gear Solid Delta Ahead of Release
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoApple Expands Self-Service Repair Program to Canada
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSnapmaker U1 Color 3D Printer Redefines Speed and Sustainability
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoAION Folding Knife: Redefining EDC Design with Premium Materials
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoGordon Murray Automotive Unveils S1 LM and Le Mans GTR at Monterey
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSolve Today’s Wordle Challenge: Hints and Answer for August 19









