Education
US High School Students Struggle as Math and Reading Scores Plummet
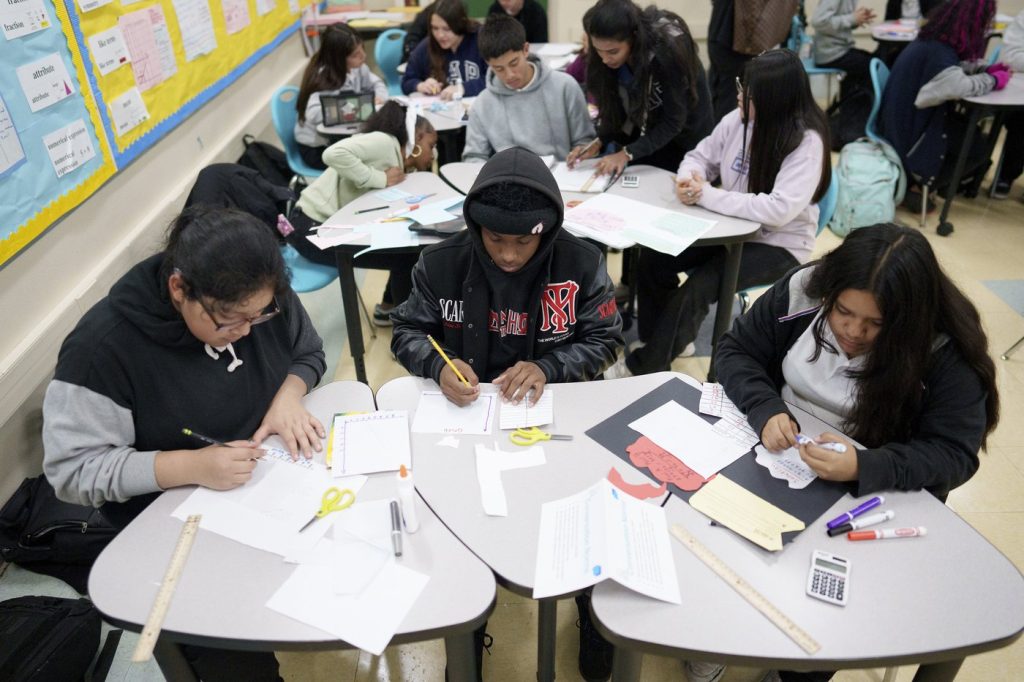

The performance of U.S. high school students in reading and math has continued to decline, with 12th graders recording their lowest scores in over two decades. Results from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), released on March 15, 2024, reveal that the troubling trend has persisted throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, raising concerns about the future of education in the country.
The assessments, which also included eighth graders’ science skills for the first time since the pandemic, indicate a significant downward trajectory across various grade levels and subjects. “Scores for our lowest-performing students are at historic lows,” stated Matthew Soldner, acting commissioner of the National Center for Education Statistics. He emphasized the need for focused action to enhance student learning.
While the pandemic undeniably impacted academic performance, experts argue that the decline in scores is part of a broader trend that predates COVID-19. Factors such as increased screen time, shorter attention spans, and a reduction in exposure to longer texts both in and out of school may be contributing to this decline. Carol Jago, associate director of the California Reading and Literature Project at UCLA, noted a significant shift in English language instruction, with many classes now assigning only three books per year, compared to 20 two decades ago.
Declining Proficiency Levels
The NAEP results highlight a stark reality: a growing number of students are failing to reach what is considered “basic” achievement levels. In reading, the average score for high school seniors in 2024 was the lowest since the assessment began in 1992, with 32% of seniors scoring below basic proficiency. In math, 45% of students also fell below this standard, marking the highest percentage since 2005.
Additionally, only 33% of high school seniors demonstrated readiness for college-level math, a decline from 37% in 2019. These figures imply that students are entering adulthood with fewer skills and less knowledge than their counterparts from a decade ago, a troubling trend given the increasing demands of the modern workforce.
Widening Achievement Gaps
The NAEP results reveal a widening gap between the highest- and lowest-performing students, particularly in eighth-grade science. This disparity reflects the growing inequality within the U.S. education system. The achievement gap in 12th-grade math has also expanded, indicating that systemic issues are exacerbating educational inequality.
Moreover, the results have uncovered a resurgence of the gender gap in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) courses. In 2019, boys and girls had nearly equal scores on the NAEP science assessment, but by 2024, girls experienced a more significant decline. This pattern is echoed in state math assessments, suggesting that programs designed to engage girls in these subjects have faltered post-pandemic.
The impact of the pandemic on educational practices cannot be understated. The disruption of hands-on learning experiences essential for grasping scientific concepts has been significant, as noted by Christine Cunningham, senior vice president of STEM learning at the Museum of Science in Boston. Nonetheless, she pointed out that declines in performance began before school closures in 2020.
As the education community grapples with these challenges, Linda McMahon, Education Secretary, underscored the need for reform, stating that despite substantial annual funding for K-12 programs, achievement gaps are widening. “More high school seniors are performing below the basic benchmark in math and reading than ever before,” she remarked, calling for increased state control over education spending.
The latest NAEP results present a critical snapshot of the state of education in the United States, emphasizing the urgent need to address the factors contributing to declining student performance. As educators, policymakers, and communities reflect on these findings, the focus will need to shift toward strategies that foster resilience and adaptability among students in an increasingly complex world.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoToyoake City Proposes Daily Two-Hour Smartphone Use Limit
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoPedestrian Fatally Injured in Esquimalt Collision on August 14
-
 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoB.C. Review Reveals Urgent Need for Rare-Disease Drug Reforms
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDark Adventure Game “Bye Sweet Carole” Set for October Release
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoJimmy Lai’s Defense Challenges Charges Under National Security Law
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoVictoria’s Pop-Up Shop Shines Light on B.C.’s Wolf Cull
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoKonami Revives Iconic Metal Gear Solid Delta Ahead of Release
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoApple Expands Self-Service Repair Program to Canada
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSnapmaker U1 Color 3D Printer Redefines Speed and Sustainability
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoAION Folding Knife: Redefining EDC Design with Premium Materials
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoGordon Murray Automotive Unveils S1 LM and Le Mans GTR at Monterey
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSolve Today’s Wordle Challenge: Hints and Answer for August 19









