Science
Breakthrough Discovery Changes Understanding of Plant Hormone Production
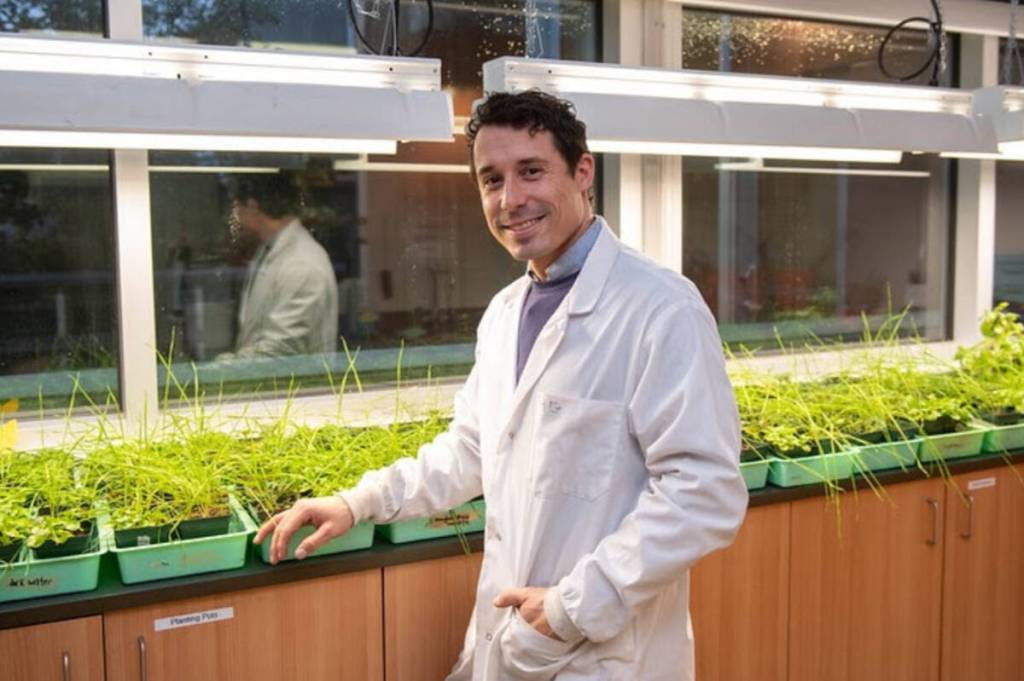

A significant advancement in plant science has emerged from the research of biochemist Harley Gordon and his team at the University of the Fraser Valley (UFV). Their recent study has unveiled a novel method for synthesizing phytohormones, particularly focusing on the role of salicylic acid, a crucial hormone in plant health. This finding has profound implications for understanding how plants respond to environmental stressors such as pests and diseases, as well as for enhancing crop resilience.
Salicylic acid is one of the six primary hormones that regulate plant growth and development. According to Gordon, “Plants, like humans, rely on hormones to do all sorts of things. They are sessile, meaning they cannot escape stressors. During stressful times, such as drought or frost, they often experience spikes in hormone concentrations, leading to biochemical changes as they adapt or defend themselves.”
Gordon’s research primarily involved the plant species Arabidopsis, commonly known as thale cress, which has been a staple in plant studies. However, the team’s findings revealed a surprising fact about this model organism. “Prior to our work, the existing knowledge about salicylic acid synthesis was heavily based on Arabidopsis literature. It turns out they are an anomaly; they have lost the ability to synthesize salicylic acid in the way most plants do,” he explained.
This revelation suggests that much of the previous research on salicylic acid might be flawed, as it relied on data from Arabidopsis rather than a broader range of plant species. This is a crucial development, as it could significantly alter the approach scientists take to enhance stress tolerance in crops and fruit-bearing plants.
Moreover, understanding salicylic acid production has implications beyond agriculture. The hormone is part of extracts that have historically been used in pain relief medicines. The study’s findings may inform future applications in human healthcare as well.
The research conducted by Gordon and his team has received validation from two additional studies published around the same time, confirming the significance of their discovery. This collaborative affirmation underscores the importance of their work in reshaping the understanding of plant hormone dynamics.
As scientists continue to explore the complexities of plant biology, Gordon’s research provides a fresh perspective on the synthesis of salicylic acid, paving the way for innovations in agriculture and potential advancements in medical applications. The implications of this study extend far beyond the laboratory, offering new pathways for improving both plant and human health.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoToyoake City Proposes Daily Two-Hour Smartphone Use Limit
-
 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoB.C. Review Reveals Urgent Need for Rare-Disease Drug Reforms
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoPedestrian Fatally Injured in Esquimalt Collision on August 14
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDark Adventure Game “Bye Sweet Carole” Set for October Release
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoJimmy Lai’s Defense Challenges Charges Under National Security Law
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoVictoria’s Pop-Up Shop Shines Light on B.C.’s Wolf Cull
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoKonami Revives Iconic Metal Gear Solid Delta Ahead of Release
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoApple Expands Self-Service Repair Program to Canada
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSnapmaker U1 Color 3D Printer Redefines Speed and Sustainability
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoAION Folding Knife: Redefining EDC Design with Premium Materials
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSolve Today’s Wordle Challenge: Hints and Answer for August 19
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoGordon Murray Automotive Unveils S1 LM and Le Mans GTR at Monterey









