Science
Scientists Unveil Secrets of Beer Foam Stability After Seven-Year Study
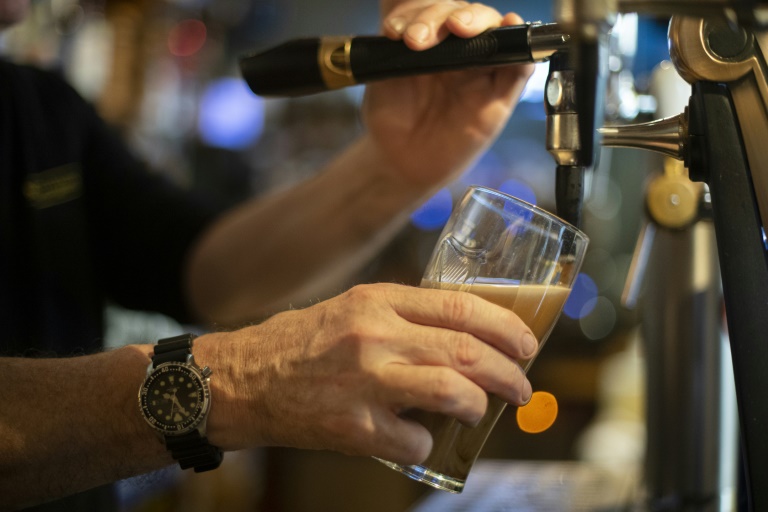

Researchers at ETH Zurich have made significant strides in understanding the science behind beer foam stability, revealing why certain beers maintain a thicker layer of foam for longer periods. This study, which unfolded over seven years, highlights how the unique physical mechanisms in different beer styles influence the longevity of their foam.
For many beer enthusiasts, the experience of enjoying a beverage is often enhanced by a creamy foam topping. Unfortunately, this foam can quickly dissipate, leaving drinkers wondering about its fleeting nature. Some beer varieties, particularly those from Belgium, are noted for their ability to sustain foam, prompting researchers to explore the underlying reasons.
The inquiry into foam stability began with a straightforward question posed to a Belgian brewer: “How do you control brewing?” The response was succinct yet insightful: “By watching the foam.” This comment sparked a comprehensive investigation into the forces that contribute to enduring beer foam.
Understanding the Physics Behind Foam
In their analysis, scientists examined various Belgian ales, discovering a clear order of foam stability. The research indicated that “Tripel” beers yielded the most stable foam, followed closely by “Dubbel” beers, while “Singel” beers displayed the least durability. This pattern can be attributed to factors such as fermentation levels and alcohol content.
Additionally, the team evaluated two leading lagers from Swiss breweries. Although these lagers demonstrated foam stability comparable to that of Belgian ales, the underlying physics differed significantly, with one lager performing notably worse.
For years, it was believed that the stability of beer foam was primarily due to protein-rich layers forming around each bubble. These proteins, derived from barley malt, affect the bubble’s surface viscosity and tension. However, the recent findings indicate that foam stability is influenced more intricately by beer style and specific protein interactions.
Key Factors Influencing Foam Longevity
The research delved into how proteins and surface forces contribute to foam stability. In lager beers, stability hinges on surface viscoelasticity, which is significantly influenced by the quantity of protein present and the denaturation process. When protein levels are elevated, they create a sturdier film around the bubbles, thus prolonging foam duration.
Conversely, “Tripel” beers rely less on surface viscoelasticity. Instead, they maintain their foam through Marangoni stresses, which are generated by variations in surface tension across the liquid. This phenomenon was initially identified in the “tears of wine” effect, illustrating the complexity of foam dynamics.
The researchers discovered that the stability of foam is closely linked to the structure and behavior of the protein-rich shells enveloping each bubble. In Belgian “Singel” beers, these shells exhibit behavior akin to a tightly packed arrangement of small spherical particles. This arrangement resembles a two-dimensional suspension, assisting in foam retention.
On the other hand, “Dubbel” beers display a mesh-like membrane formed by proteins, adding further strength to the bubbles. The “Tripel” beers again stand apart, with bubble dynamics akin to those of common surfactants used to stabilize foams in various products.
While the study provides valuable insights into foam stability, the precise reasons behind these variations are yet to be fully delineated. One protein, LTP1, appears to play a critical role, but the relationship between protein levels and foam stability is not linear. For instance, increasing surfactants to boost viscosity could inadvertently destabilize foam due to interference with Marangoni effects.
The comprehensive research findings are documented in the journal Physics of Fluids under the title “The Hidden Subtlety of Beer Foam Stability: A Blueprint for Advanced Foam Formulations.” This work not only enriches the understanding of beer brewing but could also have implications for industries that rely on foam stability in their products.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoToyoake City Proposes Daily Two-Hour Smartphone Use Limit
-
 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoB.C. Review Reveals Urgent Need for Rare-Disease Drug Reforms
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoPedestrian Fatally Injured in Esquimalt Collision on August 14
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDark Adventure Game “Bye Sweet Carole” Set for October Release
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoJimmy Lai’s Defense Challenges Charges Under National Security Law
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoVictoria’s Pop-Up Shop Shines Light on B.C.’s Wolf Cull
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoKonami Revives Iconic Metal Gear Solid Delta Ahead of Release
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoApple Expands Self-Service Repair Program to Canada
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSnapmaker U1 Color 3D Printer Redefines Speed and Sustainability
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoAION Folding Knife: Redefining EDC Design with Premium Materials
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSolve Today’s Wordle Challenge: Hints and Answer for August 19
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoGordon Murray Automotive Unveils S1 LM and Le Mans GTR at Monterey









