Science
Winnipeg Researcher Contributes to Potential Mars Life Discovery
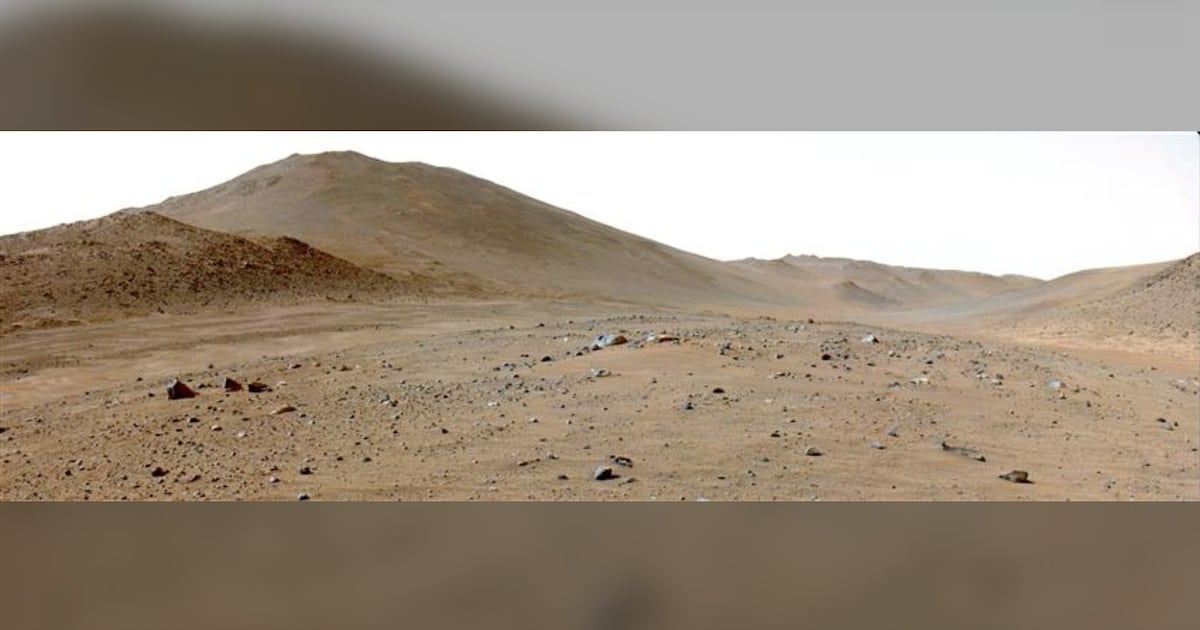

A team of researchers, including Ed Cloutis from the University of Winnipeg, has potentially identified signs of life on Mars. Their study focuses on samples collected by NASA‘s Perseverance Mars Rover from an area believed to be an ancient river channel on the planet. The findings reveal that rocks on Mars contain crucial minerals and elements, such as carbon, that are essential for sustaining life.
Cloutis, who has been involved in Mars exploration for over three decades, commented on the study’s implications. “There are many signs that indicate that even if life wasn’t there, it was at least habitable,” he stated. This suggests that while the current Martian environment is inhospitable, conditions billions of years ago may have been significantly more conducive to life.
As Cloutis explained, the prevailing theory among scientists is that Mars once resembled Earth more closely than it does today. “The suggestion is there could have been life there, but it’s probably long dead,” he noted. The research team’s analysis indicates that ancient environmental conditions may have supported life, but further examination of the samples is necessary before drawing definitive conclusions.
Significant Findings from Mars Exploration
The Perseverance rover, which landed on Mars in February 2021, is tasked with seeking signs of ancient microbial life and collecting rock and soil samples for future return to Earth. The latest findings mark a significant step in understanding the planet’s history and its potential to have harbored life. Cloutis remarked on the “intriguing” nature of these results, emphasizing the importance of thorough analysis as the next phase of research unfolds.
The discovery of carbon-containing minerals is a critical aspect of this investigation. Carbon is a fundamental building block of life as we know it. Researchers are now tasked with analyzing other geological features and elements present in the samples to build a clearer picture of Mars’ past.
While the journey of understanding Mars continues, Cloutis and his team remain hopeful. They are part of a broader scientific community that is keenly interested in unlocking the mysteries of the “Red Planet.” As analysis progresses, the potential implications for our understanding of life beyond Earth could be profound.
Scientists are closely monitoring the ongoing research efforts and look forward to the insights they may yield. With every new discovery, humanity inches closer to understanding whether we are alone in the universe.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoToyoake City Proposes Daily Two-Hour Smartphone Use Limit
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoPedestrian Fatally Injured in Esquimalt Collision on August 14
-
 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoB.C. Review Reveals Urgent Need for Rare-Disease Drug Reforms
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDark Adventure Game “Bye Sweet Carole” Set for October Release
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoJimmy Lai’s Defense Challenges Charges Under National Security Law
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoVictoria’s Pop-Up Shop Shines Light on B.C.’s Wolf Cull
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoKonami Revives Iconic Metal Gear Solid Delta Ahead of Release
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoApple Expands Self-Service Repair Program to Canada
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSnapmaker U1 Color 3D Printer Redefines Speed and Sustainability
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoAION Folding Knife: Redefining EDC Design with Premium Materials
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoGordon Murray Automotive Unveils S1 LM and Le Mans GTR at Monterey
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoSolve Today’s Wordle Challenge: Hints and Answer for August 19









